The issue
Around 7 million people in the U.S. have Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and that number is expected to reach 14 million by 2060 according to the CDC. This makes effective early diagnostics and treatments that modify the course of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) crucial. While amyloid plaques are a well-known pathological feature of AD, growing evidence suggests that the harmful effects of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide oligomers (oligomers – low molecular weight polymers comprising a small number of repeat units whose physical properties are significantly dependent on the length of the chain) begin well before plaque formation. These toxic oligomers are found in both transgenic mouse models and human AD brains, where their presence is linked to synaptic dysfunction and memory impairment—unlike plaque accumulation, which shows no such correlation. Notably, the emergence of Aβ oligomers is the earliest detectable biochemical event in the development of amyloid pathology, occurring before tau phosphorylation, plaque buildup, neurofibrillary tangles, and overall neurodegeneration.
The new test

Fujirebio is a multinational biotechnology company based in Tokyo, Japan. They have around 25 years of experience in creating diagnostic solutions for AD. Their Lumipulse G pTau217/β-Amyloid 1-42 Plasma Ratio test measures two proteins—pTau217 and β-amyloid 1-42—found in human plasma, a component of blood. It calculates the ratio between these proteins, which correlates with the presence or absence of amyloid plaques in the brain, potentially reducing the need for PET scans. Similar FDA-authorized or cleared tests, including one from the same company, rely on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) obtained through an invasive lumbar puncture (spinal tap). Because of this the FDA granted Lumipulse the 510(k) premarket notification pathway. This involves submitting documentation to the FDA to show that a new medical device is substantially equivalent to an existing, legally marketed device, known as a predicate. Lumipulse also received the Breakthrough Device designation—a program intended to accelerate the development and review of devices that offer more effective diagnosis or treatment for serious or irreversibly debilitating diseases or conditions.
pTau217 – Brief Background
p-Tau217 refers to the tau protein—essential for maintaining the structure and function of neurons—that has been phosphorylated at the 217th amino acid residue. Elevated levels of p-Tau217 have been detected in both plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, even during the early stages of the condition. However, only specific forms of p-tau—not all—are linked to neurofibrillary tangle pathology (NFT), the second key hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. NFT’s are caused by hyperphosphorylated tau protein inside neurons, causing their dysfunction. As a result, p-tau-especially 217 is considered the leading blood-based biomarker for detecting AD pathology across all stages of the disease.
β-Amyloid 1-42 Brief Background
The primary component of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques in Alzheimer’s disease is the Aβ peptide. This peptide is generated through the sequential cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase 1 (BACE1) and a complex of γ-secretases. APP is a transmembrane protein found in the plasma membrane and various organelles of neurons, glial cells, and other peripheral tissues. This cleavage process produces peptides consisting of either 40 or 42 amino acids, known as Aβ40 and Aβ42, respectively. The Aβ42 peptide, with its two additional amino acids, has a greater tendency to aggregate, making it the most “amyloidogenic” form. This mechanism became clearer after the first case of familial early-onset Alzheimer’s disease (EOAD) was linked to mutations in the APP gene, which led to increased production of Aβ42 peptides.
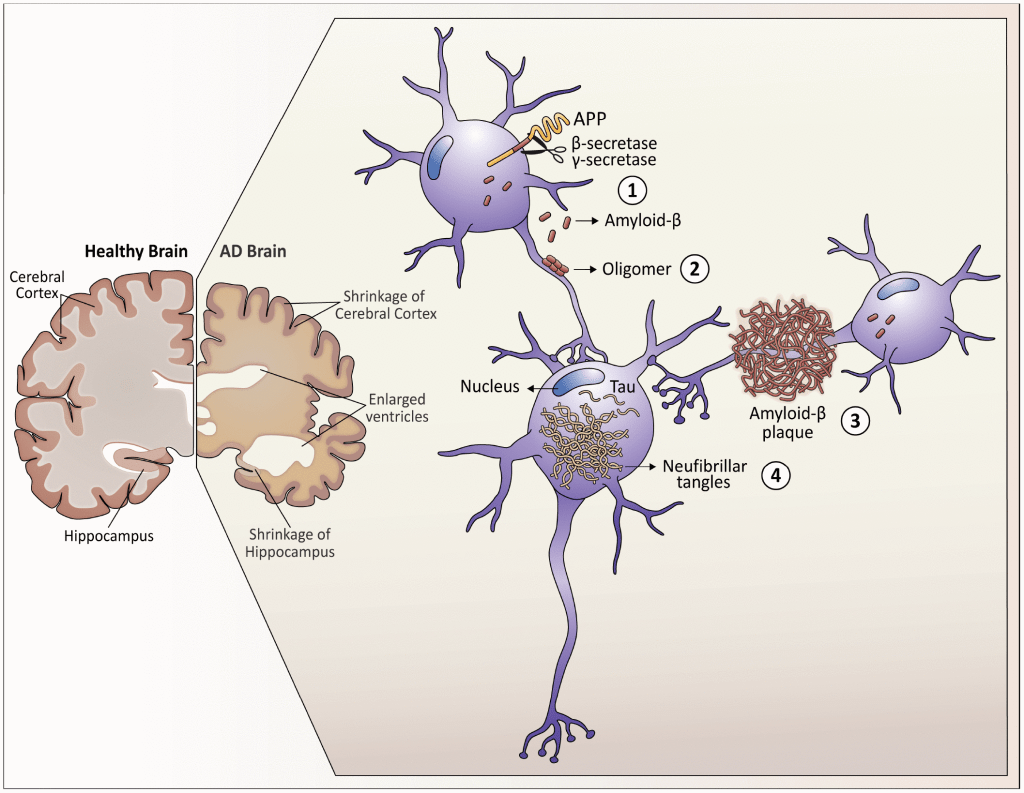
– Diagram showcasing neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
#1 Advantage of this test
This new Lumipulse test requires only a standard blood draw, making it significantly less invasive and more accessible for patients. Generally to get an AD diagnosis is invasive, time consuming and involves high tech equipment to run tests such as the brain positron emission tomography (PET) scan – a type of imaging test used to examine brain activity. Another method, called a spinal tap, involves collecting fluid from the spine and can also be used for diagnostic purposes. In an interview with ABC news, Dr. Leah Croll, an assistant professor of neurology at SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University had this to say about Lumipulse:
“This blood test will allow primary care providers to start the diagnostic process, which is meaningful because patients typically wait months to be evaluated by a neurologist”
The FDA assessed data of the Lumipulse G pTau217/β-Amyloid 1-42 Plasma Ratio, from a multi-center clinical study involving 499 plasma samples from cognitively impaired adults. The samples were analyzed using the Lumipulse test and compared to results from either amyloid PET scans or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests. The study found that 91.7% of individuals who tested positive with the Lumipulse assay also showed the presence of amyloid plaques according to PET or CSF results. Meanwhile, 97.3% of those with negative Lumipulse results had corresponding negative findings on PET or CSF tests. Fewer than 20% of participants received an indeterminate result from the Lumipulse test.
These outcome showcases that Lumipulse can accurately determine the presence or absence of amyloid pathology linked to Alzheimer’s disease in cognitively impaired patients at the time of testing. It is intended for use in specialized care settings for individuals showing signs and symptoms of cognitive decline. The test results should be interpreted alongside other clinical information about the patient. Though the blood test has been cleared by FDA, a statement released by the agency warns it is not always accurate – “False negative results could result in additional unnecessary diagnostic tests and potential delay in effective treatment. Importantly, the Lumipulse G pTau217/ß-Amyloid 1-42 Plasma Ratio is not intended as a screening or stand-alone diagnostic test and other clinical evaluations or additional tests should be used for determining treatment options.”
Leave a comment