Sanofi has completed its purchase of Vigil Neuroscience, which was developing a small molecule targeting TREM2 to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Vigil had reached the last year of its cash runaways, and Sanofi pulled the trigger. In June 2024, the French pharmaceutical company Sanofi invested $40 million in Vigil, securing exclusive first negotiation rights to license the biotech’s small molecule TREM2 agonist. While the funding extended Vigil’s financial runway into 2026, the company faced high cash burn rates. Ultimately, Vigil warned investors, expressing significant doubt about its ability to remain operational over the following year.
This comes after everyone in the neurodegenerative space eagerly awaited what would happen in the Phase 2 study of a TREM2-activating antibody co-developed by Alector and AbbVie, which yours truly worked on. Unfortunately, the endpoints to validate its efficacy weren’t met, and the program ended. Takeda and Denali Therapeutics also shut down the development of their TREM2 antibody after the Phase 1 readout.
TREM2 background in ad
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is a transmembrane receptor found on microglia that functions as an environmental sensor for cellular damage within the central nervous system. It plays a vital role in regulating microglial activity in healthy and diseased states. Large-scale genome-wide association studies have linked increased Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk to several genes, including TREM2, which is predominantly or exclusively expressed in microglia-highlighting the significant involvement of these immune cells in the development of AD.
Research has demonstrated that genetic variants of TREM2 substantially impact AD risk. Specifically, loss-of-function variants are associated with earlier onset of symptoms and more rapid cognitive decline compared to individuals without such variants. This growing body of evidence supports the development of pharmacological agonists targeting TREM2 as a promising therapeutic strategy.
VG-3927 mechanism of action
VG-3927 is Vigil’s small molecule agonist targeting TREM2, a receptor predominantly found on microglia in the brain. Research indicates that TREM2 plays a role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, with individuals carrying rare TREM2 variants showing a higher risk of developing the condition. Scientists have also demonstrated that TREM2 clears toxic substances and abnormal proteins from the brain.
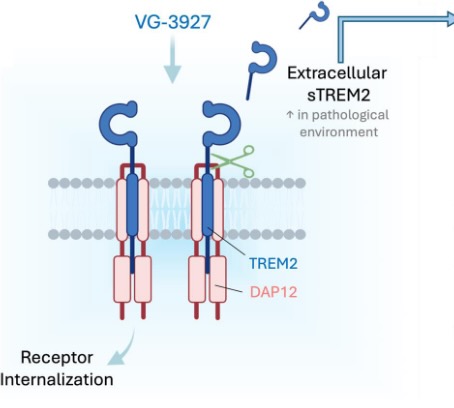
VG-3927, Vigil’s lead candidate, is a highly potent, selective, brain-penetrant oral small molecule that activates TREM2. Its mechanism of action includes promoting the internalization of the TREM2 receptor complex, which helps prevent cleavage of its extracellular domain and reduces levels of soluble TREM2 (sTREM2). Unlike antibody-based approaches, Vigil’s small molecule TREM2 agonists—including VG-3927—do not bind to sTREM2, avoiding the “sink effect” that can reduce therapeutic efficacy. By enhancing TREM2 signaling, VG-3927 is believed to support microglial function and activate neuroprotective pathways to slow disease progression in Alzheimer’s.
alzheimer’s drug market forecast
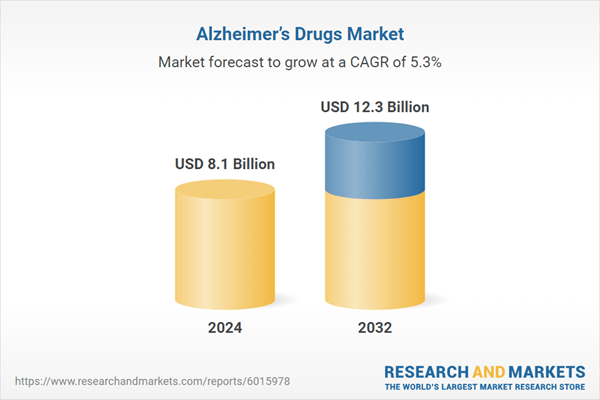
The Alzheimer’s drugs market was valued at USD 7.7 billion in 2023, fueled by a growing aging population and increased awareness of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias across the eight major markets. The market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2024 to 2032, with its value expected to reach approximately USD 12.3 billion by 2032. This is reassuring to hear, even with such a complex disease to target. The introduction of larger players in the neurodegenerative disease space, such as Biogen, AbbVie, and Novartis, has allowed for research to accelerate with these pouring funds and assets and contributing to mergers and acquisitions of smaller biotech companies working on developing neurodegenerative assets. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are common in the Alzheimer’s drugs market, designed to harness shared expertise and expedite the drug development process. These efforts are key in fostering innovation and shaping the market’s competitive landscape. There is also a shift towards developing drugs that do more than halt the symptoms.
Amyloid-targeting therapies
Recent advancements have led to the development and approval of monoclonal antibodies that target amyloid-beta. This protein accumulates abnormally in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. Notably, drugs like lecanemab and donanemab have demonstrated the ability to reduce amyloid plaques and modestly slow cognitive decline in early-stage Alzheimer’s patients. Lecanemab received traditional FDA approval in July 2023 after showing a 27% reduction in cognitive decline over 18 months in a Phase 3 trial. Donanemab, approved in Australia in May 2025, showed similar benefits but is currently indicated only for patients with early-stage disease and specific genetic profiles due to risks like brain swelling and bleeding.
tau-targeting therapies
Significant progress has also been made in developing therapies that target tau pathology. Therapies targeting tau aim to prevent or reduce the formation of neurofibrillary tangles that disrupt neuronal function. UCB Pharma’s bepranemab, a monoclonal antibody targeting extracellular tau, has shown promise in slowing tau accumulation in a subset of patients with low baseline tau levels and without the ApoE4 mutation. This suggests that tau-targeting therapies may be more effective in specific patient populations
| Main Market drivers | Main challenges |
| Progress in genomics and biomarker research is paving the way for therapies customized to a patient’s unique genetic makeup and specific disease subtypes. | High cost of drug development |
| Rise of combination therapies – pairing existing medications with novel therapeutic agents to improve overall treatment effectiveness. | Regulatory hurdles – Due to the complexity of Alzheimer’s disease, drugs in this space must meet strict regulatory standards, requiring extensive data on long-term safety and effectiveness. These regulatory challenges can lead to delays in approval and higher development costs. |
| Advancements in research and development are driving progress in the Alzheimer’s drug market. Deeper insights into the disease’s underlying mechanisms have led to the emergence of innovative drug candidates and new therapeutic targets, fueling continued market expansion. | Lack of treatments that modify the disease’s course. |
| There is increasing support from both government and non-governmental organizations—through funding, grants, and public awareness initiatives—is playing a crucial role in advancing innovation and the development of new Alzheimer’s treatments. | Maintaining patient adherence to treatment plans is a significant challenge in Alzheimer’s care, especially due to the cognitive decline linked with the disease. Poor compliance can reduce treatment effectiveness and hinder overall market growth. |
| Rising investment from pharmaceutical companies and research institutions is accelerating the development of Alzheimer’s treatments. | The Alzheimer’s drug sector is fiercely competitive, with many pharmaceutical and biotech companies striving to capture market share. This heightened competition often results in pricing pressures and difficulties in distinguishing products. |
future opportunities
| Emerging Drug Classes | There is an increasing emphasis on developing disease-modifying therapies that target key Alzheimer’s pathologies, such as amyloid-beta plaques and tau proteins. Success in these areas could revolutionize the market by offering treatments that tackle the root causes of the disease. |
| Personalized Medicine | Advances in genomics and personalized medicine are enabling the creation of treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles. This approach has the potential to improve treatment effectiveness while minimizing side effects, opening new avenues in the market. |
| Combination Therapies | Exploring combination therapies that address multiple pathways involved in Alzheimer’s disease may lead to more effective treatment options. Pairing existing medications with novel agents could enhance overall therapeutic outcomes. |
| Technological Innovations | New drug delivery technologies, including oral dissolvable films and advanced intranasal methods, promise to boost patient adherence and increase drug efficacy. |
| Global Market Expansion | With growing awareness of Alzheimer’s and improvements in healthcare infrastructure across emerging markets, there is substantial potential for market growth. Companies that successfully enter and operate in these regions can access valuable new revenue opportunities. |
Leave a comment